Germany Government#
Germany operates as a federal parliamentary republic.
National level#
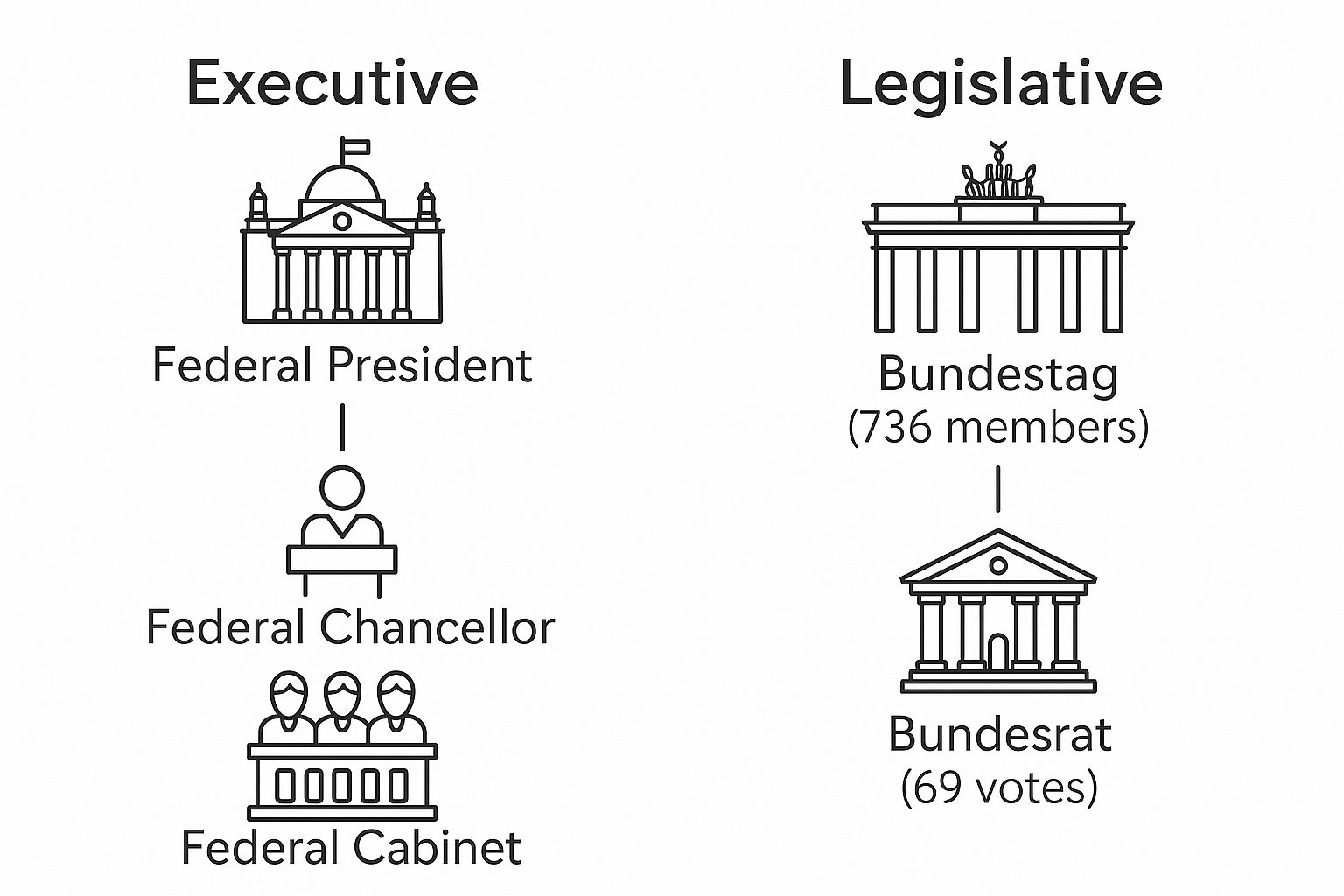
Executive branch#
The head of the German executive branch is the Federal Chancellor, who leads the federal government. The Federal President serves as head of state with largely ceremonial duties. The Chancellor appoints federal ministers who head the various federal ministries and form the Federal Cabinet. The Chancellor is elected by the Bundestag and requires a majority vote. While members of this chamber are generally not maintained by Melissa, we do maintain the Federal Chancellor, who is part of the Bundestag, and other ministers in the cabinet could also technically be members of the Bundestag.
Legislative branch#
Federal lawmaking in Germany falls to a bicameral system comprised of two chambers:
Bundestag (Federal Parliament) - The lower house with 630 members currently (minimum 598) elected every 4 years through mixed-member proportional representation from 299 constituencies.
Bundesrat (Federal Council) - The upper house with 69 members appointed by state governments to represent state interests at the federal level. It operates as a continuous body with no fixed terms.
Together, these chambers work to pass federal laws, with the Bundestag having primary legislative authority and the Bundesrat representing state interests.
Election Events#
We track federal elections and by-elections.
Level |
Chamber |
Term lengths |
|---|---|---|
National |
Bundestag |
4 years |